test for hamstring tear|physical exam for hamstring tightness : fabrication Grade 1: A mild muscle pull/strain. Grade 2: A partial muscle tear. Grade 3: A complete muscle tear. Who is most likely to injure their hamstring? Athletes, especially those who jump, climb .
For smartphones, Android tablets and iPad/iPhone. Supports HTML5, Flash, MP4. Content Security Policy
{plog:ftitle_list}
webM Garcia-Herranz, E Moro, M Cebrian, NA Christakis, JH Fowler. PLoS ONE 9 (4), e92413, 2012. 131: 2012: From seconds to months: an overview of multi-scale dynamics of mobile telephone calls. J Saramäki, E Moro. The European Physical Journal B .
A hamstring tear, also known as a rupture, infers a more serious injury. Some hamstring injuries are mild and improve with rest and over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers and pain relief creams. Others are more severe .A systematic review by Reiman et al examined clinical tests for hamstring injuries. Diagnosis can be made clinically with ecchymosis in the posterior thigh, tenderness over the hamstring muscles and avoidance of knee extension. Diagnosis can be confirmed with MRI. Treatment is generally conservative .
A hamstring tear injury is a rip in the hamstring muscles. It happens when the hamstrings are overstretched or overloaded with too much weight. Depending on the injury, the hamstring can.
special tests for hamstring strain
Hamstring strain assessment (video) These include the straight leg raise (also called Lasègue test), resisted knee flexion, and the slump test. For more severe hamstring tears an MRI scan can help determine the exact .Grade 1: A mild muscle pull/strain. Grade 2: A partial muscle tear. Grade 3: A complete muscle tear. Who is most likely to injure their hamstring? Athletes, especially those who jump, climb . Hamstring injury risk factors include: Sports. Sports that require sprinting or running might make a hamstring injury more likely. So might other activities that can require extreme stretching, such as dancing. Earlier hamstring injury. People who have had one hamstring injury are more likely to have another one. Several terms, including posterior thigh injury, hamstring strain, hamstring tendinopathy, and hamstring tear, are used to describe such injuries, but they are not always synonymous. In most cases, the severity of the injury determines treatment and the amount of time the athlete must take off from sport [ 1-9 ].
Higher quality research studies are needed to investigate the use of special tests in the diagnosis of hamstring injuries. The lack of high-quality evidence reiterates the importance of combining various tests results with a . Hamstring muscle injuries are common, especially in athletes. Most often, hamstring muscle injuries are partial tears of the muscle. These types of injuries, called muscle strains, occur when the fibers that make up the muscle are stretched beyond their normal limits.Symptoms of a hamstring muscle strain can include pain, bruising, swelling, and .A hamstring injury is a strain or tear to the tendons or large muscles at the back of the thigh. It's a common injury in athletes and can happen in different severities. The 3 grades of hamstring injury are: grade 1 – a mild muscle pull or strain; grade 2 – a partial muscle tear; grade 3 – a complete muscle tear
Description [edit | edit source]. Hamstring strains are caused by a rapid extensive contraction or a violent stretch of the hamstring muscle group which causes high mechanical stress. This results in varying degrees of rupture within the fibres of the musculotendinous unit. Hamstring strains are not rare in sports activities with a dynamic athletes like sprinting, jumping, touch .How are hamstring injuries evaluated and diagnosed? Your healthcare provider may be able to diagnose your hamstring injury based on the symptoms you report. They may test the tenderness and examine the swelling and bruising around your hamstring. Sometimes they may order a magnetic resonance imaging test (MRI).The most significant risk factor for an acute hamstring strain is a previous hamstring strain. 19,24,29,31,42,63 Athletes with a previous hamstring strain are twice as likely to sustain a hamstring strain. 19 One study of 74 soccer . or a positive lumbar quadrant test. 12 MRI-negative hamstring injuries should not be confused with referred .
Hamstring Strain Tests. To diagnose a hamstring strain, your doctor or physical therapist will ask specific questions about how your leg was injured. You'll also have a physical exam of the .Hamstring strain injuries: factors that lead to injury and re-injury. Sports Med. 2012;42(3):209-226. 16. Orchard J, Best TM, Verral GM. Return to play follow muscle strains. Clinical journal Sport Med. 2005;15(6):436-441. 17. Orchard J, Best TM. The management of muscle strain injuries: an early return versus the risk of recurrence.
Is hamstring tendonitis the same as a tendon tear? Tendonitis isn’t the same as a tendon tear. A tendon tear is a serious injury that causes the tendon to pull away from your hamstring muscles or bones. Severe tendon tears might require surgery. Is hamstring tendonitis the same as a hamstring strain? Strains and tendonitis both affect tendons .We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Hamstring strain injury (HSI) may result in considerable impairment, activity limitation, and participation restriction, including time lost from competitive sports. This CPG includes sports-related overloading and overstretching injuries to myofascial or musculotendinous structures in any combination of the 3 hamstring muscles (the .
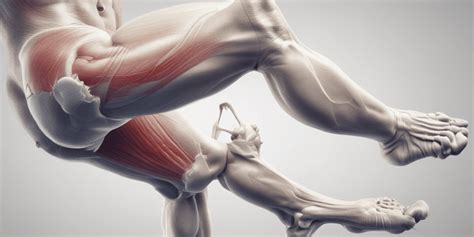
A hamstring strain, also known as a hamstring pull, is a relatively common injury that can occur in almost any sport: running, CrossFit, ice skating, and weightlifting. The injury typically happens when one of the hamstring muscles (which are located in the posterior or back of the thigh) become overloaded. This causes a strain or small tear of the muscle and a . If you have had a hamstring strain, your PT will likely progress you through exercises, similar to this program, to help you fully recover. Check in with your physical therapist to start on your own personalized rehab program .
Hamstring injuries are common, especially among athletes where they make up more than a third of all muscle traumas. But depending on the severity of the injury, it can be difficult to tell the difference between a pulled or strained .Hamstring strain injury (HSI) may result in considerable impairment, activity limitation, and participation restriction, including time lost from competitive sports. This CPG includes sports-related overloading and overstretching injuries to .
Synopsis: Hamstring strain injuries remain a challenge for both athletes and clinicians, given their high incidence rate, slow healing, and persistent symptoms. Moreover, nearly one third of these injuries recur within the first year following a return to sport, with subsequent injuries often being more severe than the original. This high reinjury rate .
A hamstring strain can be a difficult injury to return from. Far too often we see recurring strains. A better rehab plan can reduce this and get you back! . The hurdle test is part of a movement screen that can be helpful for bringing to light hip pathology or movement deficits in active flexion that might impact gait and running mechanics. The Tests. We spoke to doctor of physical therapy and head coach of Dubai’s CrossFit Gold Box, Eugene Babenko, about testing for weak hamstrings. “If you don’t feel your hamstrings with the . A new hamstring test to complement the common clinical examination before return to sport after injury. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 18, 1798-803. ASKLING, C. M., TENGVAR, M. & THORSTENSSON, A. 2013. Acute hamstring injuries in Swedish elite football: a prospective randomised controlled clinical trial comparing two rehabilitation protocols.A new hamstring test to complement the common clinical examination before return to sport after injury. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010 Dec;18(12):1798–803. Dijkstra HP, Pollock N, Chakraverty R, Ardern CL.
Hamstring injuries are one of the most common soft tissue injuries in athletes. 4, 8 – 10, 31, 35, 44 Treatment and management of hamstring injuries, 20, 24, 25 as well as injury prevention and return to sport, 1, 4, 6, 16, 30, 32 have received significant research effort in the past 10 years. Examination of athletes with hamstring injury has traditionally relied on . Measuring hamstring strength. The Isometric maximum voluntary contraction (MVC test) is particularly useful for sprinters, footballers, and other high-risk athletes. Also for those who have had a previous hamstring strain. This group need to be aware of the risk of recurrence. How to test hamstring strength A pulled hamstring is a muscle injury resulting from a strain or tear in one or more of the muscles at the back of the thigh. When it happens, there may be a sudden, severe pain and a popping or .
special test for hamstring tightness
For more information on hamstring strain visit:https://www.sportsinjuryclinic.net/sport-injuries/thigh-pain/back-thigh/hamstring-strainWhen a hamstring strai. The NHS grades hamstring injuries from 1-3: . grade 1 – a mild muscle pull or strain. grade 2 – a partial muscle tear. grade 3 – a complete muscle tear. However, the British Athletics .
testing knife blade hardness
special test for hamstring tear
WEB27 de jun. de 2018 · 1ª maneira: Crossbow, um arco que vem com dardos tranquilizantes. 2ª maneira: Shotgun, uma espingarda TOP. 3ª maneira: Sauna - na garagem da .
test for hamstring tear|physical exam for hamstring tightness